Designing a flawless parting line in Liquid Silicone Rubber (LSR) injection molding is vital for achieving high-quality, functional, and aesthetically pleasing components. The parting line, where the two halves of the mold meet, affects the appearance, functionality, and manufacturability of the final product.

1. Understand the Role of the Parting Line
The parting line serves as the interface between the two halves of the mold. It is where LSR material could potentially leak, leading to flash, or where misalignment could cause visual defects. Proper parting line design ensures:
- Aesthetic Quality: Seamless integration into the part’s design for minimal visibility.
- Functional Integrity: Alignment of critical features to ensure performance.
- Process Efficiency: Reduction of defects like flash and ease of demolding.
Understanding the part’s end-use requirements and balancing them with manufacturability is the foundation of a good parting line design.
2. Evaluate the Geometry of the Part
Part geometry dictates where the parting line can and should be placed. Key considerations include:
- Natural Seam Locations: Leverage edges, corners, or transitions in the design to hide it. For example, placing it along a ridge or contour can make it less noticeable.
- Symmetry: For symmetrical parts, align the parting line with the natural centerline to reduce visibility and improve moldability.
- Critical Features: Avoid placing it on functional surfaces, such as sealing areas, to maintain performance and avoid leaks or deformation.
3. Choose the Optimal Parting Line Location
The location of the parting line significantly affects the outcome of the molding process. Selecting the right location involves balancing several factors:
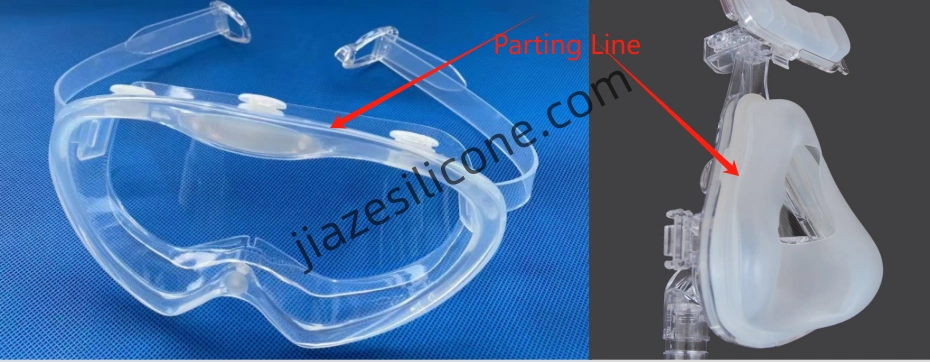
- Aesthetic Considerations: For consumer-facing parts, place them in less visible areas or blend them into the design.
- Ease of Demolding: It should support smooth ejection. Avoid locations that may cause undercuts or create challenges in removing the part without deformation.
- Alignment of Features: Ensure that critical features, such as holes, bosses, or threads, align perfectly to avoid assembly or functional issues.
When possible, use software tools like CAD and mold flow simulation to visualize and optimize the placement of it.
4. Minimize Flash
Flash, the excess material that escapes along the parting line, is one of the primary challenges in LSR molding. Minimizing flash requires a combination of design, material, and process optimizations:
- Mold Precision: Ensure that the mold halves fit together with tight tolerances, often within microns. Any gaps or misalignment can result in a flash.
- Clamping Force: Optimize clamping force during molding to prevent material leakage at it. Over-clamping can deform the mold, while under-clamping can increase flash.
- Venting: Incorporate vents near the parting line to allow trapped air to escape. Proper venting reduces pressure buildup that can force material into undesired areas.
- Material Properties: Select LSR grades with the right viscosity and flow characteristics. Low-viscosity materials are more prone to flashing if not controlled.
5. Consider Tooling Design
Tooling design plays a crucial role in achieving a flawless parting line. High-quality molds designed with precision engineering ensure long-term performance and minimal defects.
- Machining Tolerances: Use advanced machining techniques, such as CNC or EDM, to create smooth and precise mold surfaces. Achieving tight tolerances reduces flash and ensures alignment.
- Draft Angles: Incorporate draft angles into the mold design to facilitate part ejection. A lack of draft can lead to tearing or distortion.
- Interlocking Features: Consider using interlocks or alignment features, such as dowel pins or guide rails, to maintain perfect alignment between the mold halves.
- Split Line Design: Depending on the part, choose between straight or stepped parting lines. Stepped it can help in hiding the seam and improving alignment.
6. Address Material Behavior
Understanding LSR’s unique properties is critical for designing an effective parting line. LSR is a highly flowable material that cures quickly and shrinks during cooling. These factors influence its behavior:
- Flow Characteristics: Ensure that the flow of LSR within the mold does not cause uneven pressure at it, which could lead to defects.
- Shrinkage Compensation: Account for shrinkage in the mold design to ensure proper alignment and tight seals post-curing. Typically, LSR shrinkage ranges from 2-5%, depending on the grade.
- Elasticity: LSR’s flexibility makes it more forgiving during demolding, but precise control is necessary to avoid tearing at it.
7. Perform Mold Flow Analysis
Before finalizing the mold design, perform mold flow simulations to predict how the LSR will behave during the injection molding process. These simulations can:
- Identify potential areas where flash or defects might occur.
- Optimize the placement of gates and vents to control the flow of material.
- Help determine the best placement for the parting line based on pressure distribution and material flow.
8. Test and Iterate
Prototyping and testing are essential to refine the parting line design:
- Prototype Molds: Use prototype molds to test the initial design and identify issues like flash, misalignment, or aesthetic concerns.
- Trial Runs: Conduct trial runs with the production mold to evaluate its performance under real-world conditions.
- Iterative Improvements: Adjust the mold based on test results, such as reworking it to improve sealing or alignment.
9. Implement Robust Quality Control
Even the best-designed parting line can degrade over time due to wear and tear. Quality control ensures that the mold maintains its precision:
- Regular Inspections: Check the mold for signs of wear, damage, or misalignment.
- Preventative Maintenance: Schedule regular maintenance to clean and refurbish the mold, ensuring a tight seal at the parting line.
- Process Monitoring: Continuously monitor the molding process for changes in flash levels or part quality, which could indicate mold issues.
10. Leverage Automation and Advanced Technology
Modern technologies can further enhance the precision and consistency of the parting line:
- Laser Welding: Use laser welding to repair or adjust molds for precision at the parting line.
- Automated Mold Alignment Systems: These systems help maintain alignment during high-volume production.
- Advanced Mold Materials: Use durable, wear-resistant materials for the mold to reduce the impact of repeated use.
Conclusion
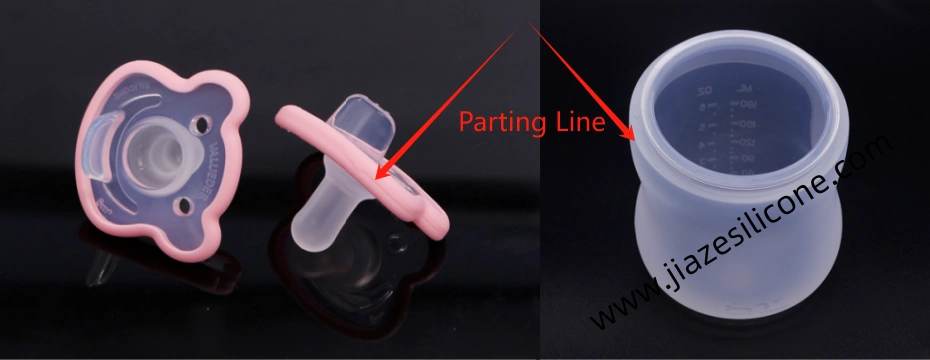
Designing a flawless parting line in LSR injection molding is a multidisciplinary task that requires balancing design, tooling, material, and processing considerations. By focusing on part geometry, minimizing flash, and leveraging advanced technologies, you can create molds that produce high-quality parts with minimal defects.
It not only enhances the aesthetic and functional qualities of the product but also ensures efficient manufacturing, reduced waste, and longer mold life. Through careful planning, simulation, and testing, manufacturers can achieve consistent results that meet the demands of modern LSR applications.